Airbnb is a community-based online platform for listing and renting local homes. It connects hosts and travelers and facilitates the process of renting without owning any rooms itself. Moreover it cultivates a sharing-economy by allowing property owners to rent out private flats.
Airbnb
Founded: 2008 / San Francisco
Tags
Story
“The world’s largest accommodation provider,
Airbnb, owns no property.”
Airbnb, owns no property.”
The Airbnb story started back in 2008, with the two founders, Joe Gebbia and Brian Chesky (Nathan Biecharczyk was invited to join later), and 3 air mattresses in San Francisco, California. Their problem: they couldn’t pay rent. They set up a simple website with a map and rented out three mattresses and promised home-made breakfast. Three people came and they decided to build on it. They refined the website with money from selling cereal boxes during the presidential campaign in 2008, and took high-quality pictures of the rented space to boost click-rates. In the winter of 2012, Airbnb overtakes Hilton Hotels in nights booked. Now, it has over 1,500,000 listings in 34,000 cities and 190 countries. Bookings can be made online and on mobile devices. In 2015, the value of the company was $25.5 billion.
Business Model
Value Proposition & Customer:
Airbnb is a community-based, two-sided online platform that facilitates the process of booking private living spaces for travelers. On the one side it enables owners to list their space and earn rental money. On the other side it provides travelers easy access to renting private homes. With over 1,500,000 listings in 34,000 cities and 190 countries, its wide coverage enables travelers to rent private homes all over the world. Personal profiles as well as a rating and reviewing system provide information about the host and what is on offer. Vice versa, hosts can choose on their own who to rent out their space to.
Airbnb is a community-based, two-sided online platform that facilitates the process of booking private living spaces for travelers. On the one side it enables owners to list their space and earn rental money. On the other side it provides travelers easy access to renting private homes. With over 1,500,000 listings in 34,000 cities and 190 countries, its wide coverage enables travelers to rent private homes all over the world. Personal profiles as well as a rating and reviewing system provide information about the host and what is on offer. Vice versa, hosts can choose on their own who to rent out their space to.
Mission & Core Values:
Airbnb is more than an affordable travelling accommodation option. Through facilitating access to distinctive spaces and local culture, Airbnb aims to enable travelers to “feel at home anywhere you go in the world” by building connections with local hosts, gaining access to distinctive spaces and culture of their destinations.
Airbnb is more than an affordable travelling accommodation option. Through facilitating access to distinctive spaces and local culture, Airbnb aims to enable travelers to “feel at home anywhere you go in the world” by building connections with local hosts, gaining access to distinctive spaces and culture of their destinations.
Value Formation & Core Activities
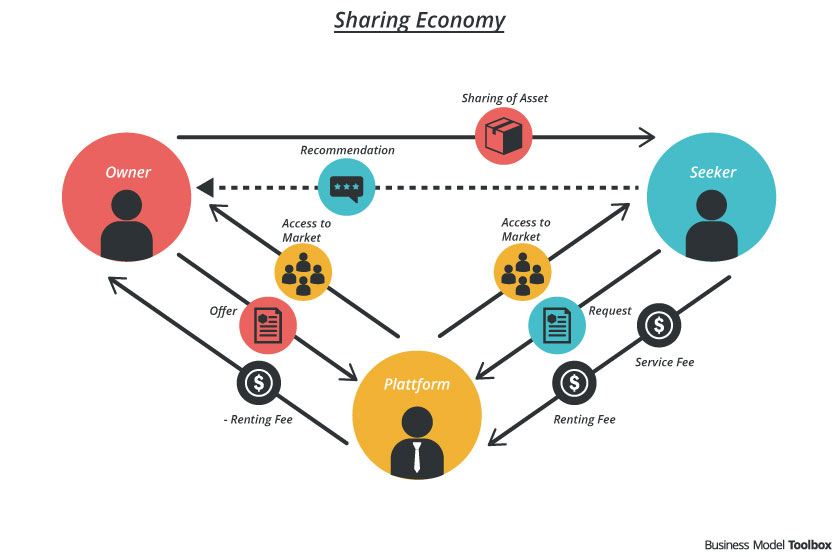
Airbnb operates as a transaction facilitator between hosts and travelers who are looking for comfortable accommodation at a cheap price. By providing host protection insurance, as well as a rating and review system, the platform builds trust within the community of users and lowers transaction costs. Profiles and user reviews help to create reputation and trust among participants of the marketplace.
Airbnb operates as a transaction facilitator between hosts and travelers who are looking for comfortable accommodation at a cheap price. By providing host protection insurance, as well as a rating and review system, the platform builds trust within the community of users and lowers transaction costs. Profiles and user reviews help to create reputation and trust among participants of the marketplace.
Revenue Model
Airbnb receives commissions from two sources upon every booking, namely from the hosts and guests. For every booking Airbnb charges the guest 6-12% of the booking fee. Moreover Airbnb charges the host 3% for every successful transaction.
Airbnb receives commissions from two sources upon every booking, namely from the hosts and guests. For every booking Airbnb charges the guest 6-12% of the booking fee. Moreover Airbnb charges the host 3% for every successful transaction.
Organisation
While Airbnb was at the Y-incubator, Paul Graham told them “it’s better to have 100 people who love you than having a million of people that sort of like you.” Therefore, Airbnb focuses on “making what people want” and cultivating a “sense of belonging”, by engaging its community through story-sharing on the Airbnb website and by inviting users to be part of its logo redesign campaign. Airbnb also interacts with the local community beyond the virtual space, through partnerships with city authorities in San Francisco and Portland in identifying hosts to help displaced people in the event of an emergency.
While Airbnb was at the Y-incubator, Paul Graham told them “it’s better to have 100 people who love you than having a million of people that sort of like you.” Therefore, Airbnb focuses on “making what people want” and cultivating a “sense of belonging”, by engaging its community through story-sharing on the Airbnb website and by inviting users to be part of its logo redesign campaign. Airbnb also interacts with the local community beyond the virtual space, through partnerships with city authorities in San Francisco and Portland in identifying hosts to help displaced people in the event of an emergency.
Challenges
Trust
As the community of users grows bigger, trust remains an issue despite the provision of insurance.
As the community of users grows bigger, trust remains an issue despite the provision of insurance.
Regulations
Many cities start to introduce laws in order to regulate the renting out of private apartments, because some hosts rent out apartments like a business without paying taxes. E.g. in November 2015, San Francisco residents voted against Proposition F, a measure that would have severely restricted short-term rentals.
Many cities start to introduce laws in order to regulate the renting out of private apartments, because some hosts rent out apartments like a business without paying taxes. E.g. in November 2015, San Francisco residents voted against Proposition F, a measure that would have severely restricted short-term rentals.
Traveler Retention
Airbnb provides offers, promotional codes and credits to frequent travelers, as well as to hosts
Airbnb provides offers, promotional codes and credits to frequent travelers, as well as to hosts
Imitators
Especially when entering a new market with its own peculiarities, local imitators could have already adjusted the business model according to local culture and established the first-comer benefits.
Especially when entering a new market with its own peculiarities, local imitators could have already adjusted the business model according to local culture and established the first-comer benefits.
Positive Impact
- Sharing Economy allows using and sharing resources without possessing them
- Revenue generation for local hosts
- Economic benefit: boost tourism in underexplored areas of cities
- After the Hurricane Sandy incident, Airbnb launched a microsite to offer free housing for persons displaced by the storm in New York City
Negative Impact
- in the long-term, the renting of entire apartments could push up rent prices –> effect on long-term housing market
- Enables property owners and investors to directly impact the housing supply. This includes not only renting rooms and apartments to tourists that have historically been rented to residents, but also includes buying and renovating real estate just for the purpose of renting to tourists.
Resources
Business Model Toolbox Ressources:
External Resources:
- Airbnb – Homepage
- Business Insider: Three challenges facing Airbnb in China
- The Atlantic: Airbnb CEO Brian Chesky on Building a Company and starting a ‘Sharing Revolution’
- Fortune: Airbnb raises $1.5 billion, valuing it at an eye-popping $25.5 billion
- Techcrunch: A brief history of Airbnb
- The Telegraph: Airbnb: the story behind the $1.3 bn room-letting website



Everything that you shared, is just amazing!