Subscription
Tags
Description
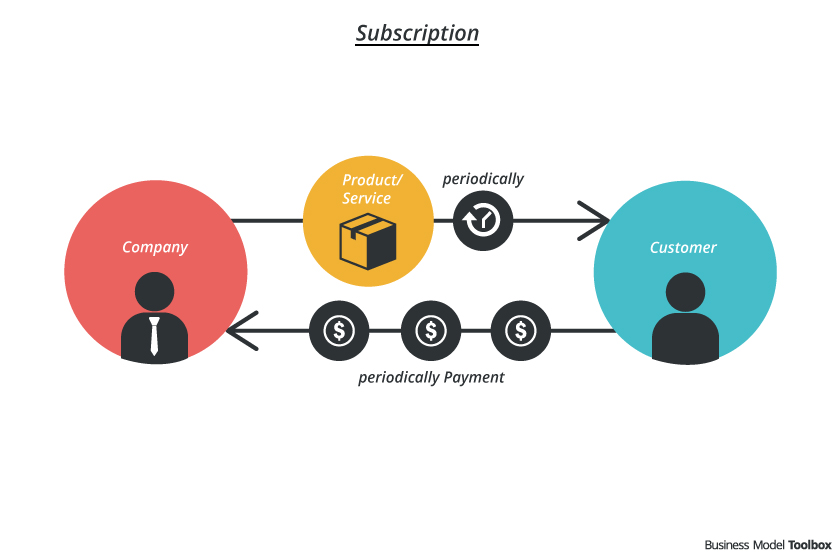
Instead of selling the product as a single item, the subscription model aims at selling a product or service over a period of time. The subscription model has been introduced by newspapers and magazines and is now used by many different products and services, which the customer can access by paying a periodic fee .
There are two different kinds of subscription models:
- The customer receives a product / service periodically: the ownership is transferred to the customer
- The customer gains access to a service or virtual product: the customer gets the right to use it (SAAS = software as a service)
Digital business models often provide a basic service for free and offer premium features together with a subscription model (LINK Freemium + Subscription pattern).
Success factors
Design the subscription experience
Don’t just think about the service or product but also about the process during the subscription phase.
Use the existing relationship to learn about the needs of your customer
Learn about how to stay attractive over time e.g. by using customer data.
Create a lock-in
Switching costs and therefore customer retention and lock-in effects increase when users enter or collect information, build up a network or invest time in the service over time.
Examples
Newspapers & magazines
Receive every issue over a period of time.
Receive every issue over a period of time.
Pay TV and on-demand video streaming
Monthly payment to get access to premium channels (Pay TV) or the possibility to stream video whenever required.
Blacksocks
Offers a subscription for black socks and underwear.
Birchbox
A service that sends its subscribers a box of four to five samples of make-up or other beauty products.
Adobe Software
The software provider changed the business model from selling the software to offering a subscription.
Chances
- Cash flow: A subscription model provides the company with a more reliable cash flow because revenue and costs for creating the product / service are more predictable
- Customer retention and reduction of seasonal fluctuation: Depending on the design of the subscription model, customers can be bound to the service over a defined period of time or cannot reject to buy one issue / delivery.
- Lock-in effect: As the service is provided on a recurring basis, there is a higher probability that the customer will stay with the company because of brand loyalty and / or high switching costs
- Attracting customers: A reasonable monthly rate seems affordable and more attractive than a one-time high payment.
Risks
- Reliable service / product delivery: It is essential to maintain or even improve the quality of the service, in order to build on the trust that customers put in the product over a longer period of time.
- Low switching costs: Affordable and attractive subscription rates make it interesting and affordable to try and compare different offers.
Responsibility
Customer Data
When using customer data to optimize the service it is important to be transparent and to respect customer privacy.
Recycle or reuse to reduce waste
Subscriptions of tangible products can lead to increased waste because customers may not need every periodical delivery. Take in mind to how to recycle or reuse your product.
Transparency
Another aspect is transparency and honesty to the customer about the conditions involved in a subscription contract. Many companies lure customers with cheap monthly rates and hide the conditions regarding not canceling in time.
Resources
- Venturebeat: Why subscription business models will transform every industry
- subscriptionschool.com: Online resource to learn “how to run a successful subscription business”