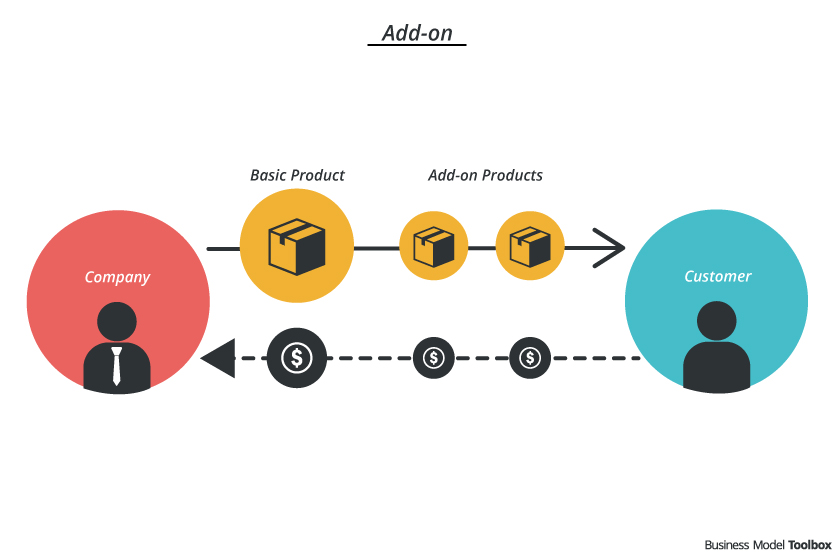
Add-on
Tags
Description
The first approach is to look at the competitive environment: if there are many competitors that offer similar solutions to a problem or when it is difficult to position a company as a quality leader the add-on pattern might be a strategy to differentiate via price. The basic product is offered at a competitive price that attracts the customers’ attention. Different extras can be added to the basic product that drive the final price. Sometimes it is even linked to a cross financing strategy: the basic product is sold below it’s actual value.
The second approach is to primarily use the add-on pattern as a part of the product & pricing strategy: it helps to guide the customer within his decision.
It is a common pattern used in the car industry: the basic car is cheap but usually buyer then start to add extras that make the car the one they really want to have.
Looking at this pattern from a inclusive point of view there is the potential that this business model pattern allows freedom to fulfill on the one hand a basic need (transportation, care,..) and on the other hand allows customization and freedom for fulfilling special needs.
Success factors
Make sure that the basic product fulfills the core needs but also creates the desire for the add ons. If this thershold is overlooked the product is simply incomplete. Use the Kano Model to explore the bottom line quality and features your product needs.
Develop a balanced pricing strategy that includes the basic product with (usually) a low or no margin and attractive add-ons with high margin.
Constantly run tests with new add-ons to keep your product fresh and to learn about changing needs or undiscovered potentials.
Buyer-seller relationships are imperative with communication, empathy and understanding of wants and needs.
Examples
You can choose a basic version of the car for a reasonable price but every extra that makes the car faster, nicer or more special means additional costs.
Low Cost Airlines
Basic air travel is very cheap but every extra needs to be purchased additionally: seat reservation, baggage, food, priority check-in. There were even rumors that even using the bathroom will be charged.
Mobile Games
You can download the game for free and purchase various add-ons in an in-app store to be more successful (e.g. additional lives, more resources, special power…)
Chances
- Customer Acquisition: a great cheap core product attracts new customers
- Customer Satisfaction: the customer can choose add-ons according to his needs. This offers the possibility to individualize the product and only pay for features that are personally important.
- Attractiveness: with new add-ons you can always keep your product innovative without changing the core product itself
Risks
- It is essential to market the add-ons as an attractive feature and as additional value.
- One must regularly remain aware of the customer’s needs in order to ensure the add-on is an appropriate one.
Responsibility
Resources
- Preferred CEO: The Add-On Business Model & Why It Works
- James Laws: What’s So Great About The Add-On Business Model
- Chron: What Is Add-On Selling?